Lipomas are benign tumors made up of fatty tissue. They are generally harmless and often do not require treatment unless they become bothersome or painful. Understanding how to identify a Lipoma Treatment In Dubai can help individuals determine whether they need medical attention. This article discusses the signs and symptoms of lipomas, their characteristics, and when to seek professional advice.
Understanding Lipomas
What is a Lipoma?
A lipoma is a slow-growing, soft, and movable lump that develops beneath the skin. Composed of adipose (fat) tissue, lipomas are usually painless and can vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. While they can occur anywhere on the body, they are most commonly found on the arms, shoulders, neck, back, and thighs. Lipomas are non-cancerous and typically do not pose any health risks.
Common Misconceptions
Although lipomas are made up of fatty tissue, they are not caused by obesity or excessive weight. People of all body types can develop lipomas, and they are generally considered harmless unless they grow large enough to cause discomfort or cosmetic concerns.
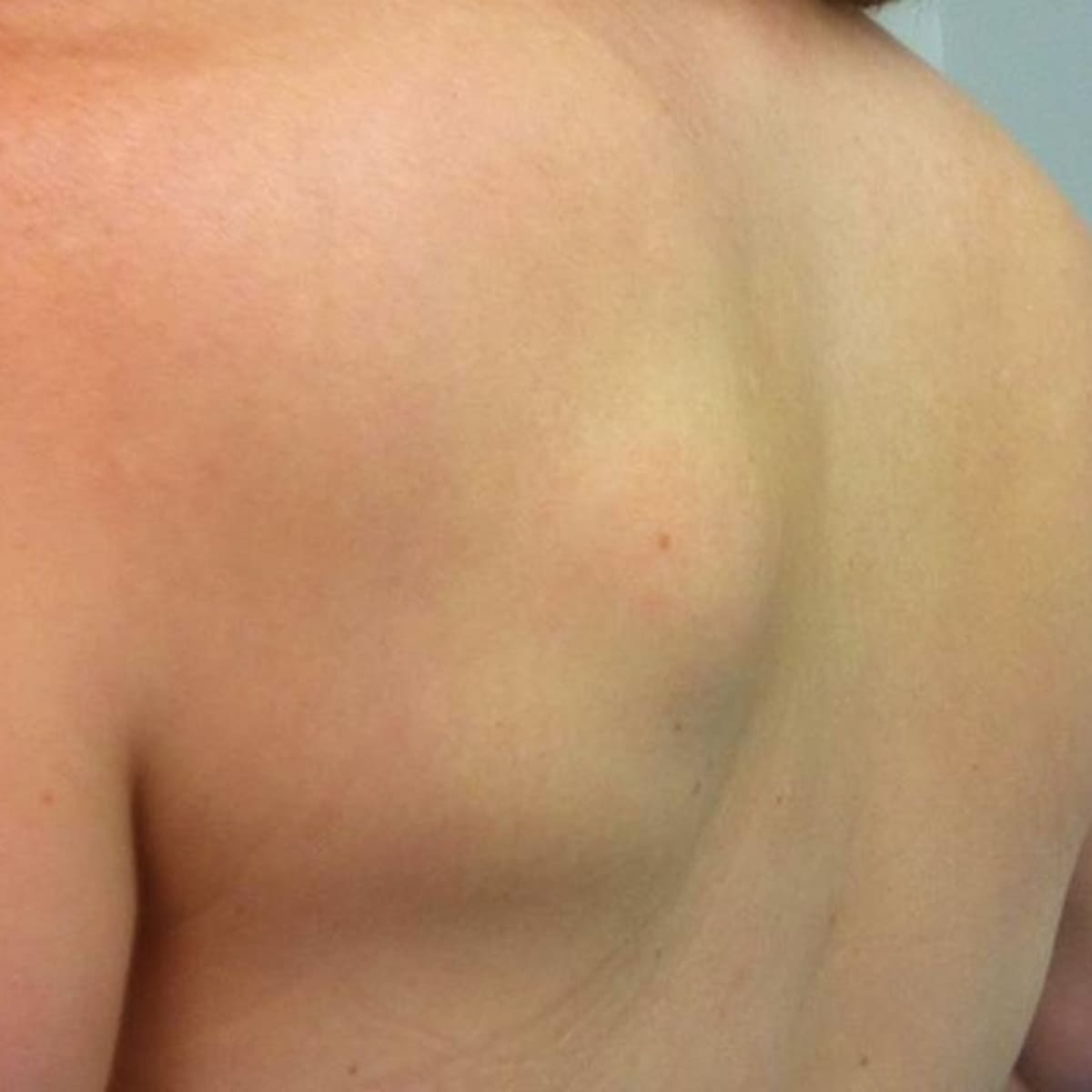
Signs and Symptoms of Lipomas
1. Appearance and Texture
Lipomas typically appear as soft, rounded lumps just beneath the skin. Key characteristics include:
Softness: Lipomas have a soft, doughy texture and can often be easily moved when pressed.
Painlessness: Most lipomas are painless, though some individuals may experience discomfort if the lipoma is located near a nerve or joint.
Size Variation: Lipomas can vary in size, ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. Larger lipomas may be more noticeable and can sometimes be mistaken for other types of lumps.
2. Location
Lipomas can develop in various locations on the body, but they are most commonly found in:
Upper Body: Including the shoulders, back, and neck.
Arms and Thighs: Often found in the limbs, especially the upper arms and inner thighs.
Abdomen: Lipomas can also occur in the abdominal area, sometimes becoming larger and more noticeable.
3. Mobility
One distinguishing feature of lipomas is their mobility. When gently pressed, a lipoma will typically move freely beneath the skin. This differentiates it from other types of lumps that may be attached to underlying tissues.
4. Gradual Growth
Lipomas usually grow slowly over time. Individuals may notice that a lump develops gradually and remains stable in size. It is essential to monitor any changes in the lump's size or appearance, as rapid growth could indicate a need for further evaluation.
When to Seek Medical Attention
1. Changes in Size or Shape
If you notice that a lipoma is changing in size or shape, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional. While most lipomas are stable, any rapid growth or sudden changes could warrant further investigation to rule out other potential conditions.
2. Pain or Discomfort
Although lipomas are generally painless, some individuals may experience discomfort if the lipoma presses against surrounding tissues or nerves. If a lipoma becomes painful or tender, it is important to seek medical advice to determine the best course of action.
3. Concerns About Appearance
Many individuals seek treatment for lipomas primarily for cosmetic reasons. If a lipoma is affecting your self-esteem or confidence, discussing treatment options with a healthcare provider can provide guidance on whether removal is appropriate.
4. Uncertainty About Diagnosis
If you are unsure whether a lump is a lipoma or if it resembles a lipoma but has other concerning features, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional. They can perform a physical examination and may recommend imaging studies, such as an ultrasound, to confirm the diagnosis.
Diagnosis of Lipomas
Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will typically begin by performing a physical examination of the lump. During this assessment, they will evaluate the size, texture, and mobility of the lump, as well as its location on the body.
Imaging Studies
In some cases, additional imaging studies may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis of a lipoma. Common imaging techniques include:
Ultrasound: This non-invasive test uses sound waves to create images of the soft tissue, allowing the provider to assess the characteristics of the lump.
MRI or CT Scan: In certain situations, more detailed imaging may be required to differentiate a lipoma from other types of tumors or growths.
Biopsy
Although it is rare, a biopsy may be performed if there is any uncertainty about the nature of the lump. A small sample of tissue is taken and analyzed to determine if it is indeed a lipoma or another type of growth.
Treatment Options for Lipomas
1. Observation
If a lipoma is asymptomatic and does not cause any discomfort or cosmetic concerns, it may be appropriate to simply monitor it over time. Regular check-ups can help ensure that there are no changes in size or appearance.
2. Surgical Removal
For individuals who experience discomfort or wish to remove a lipoma for cosmetic reasons, surgical excision is the most common treatment option. This outpatient procedure involves the following steps:
Anesthesia: The area around the lipoma is numbed with a local anesthetic.
Incision: A small incision is made to remove the lipoma and its capsule.
Closure: The incision is closed with stitches, and the area is bandaged.
3. Liposuction
In some cases, liposuction may be used to remove lipomas, particularly smaller ones. This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a thin tube to suction out the fatty tissue, leaving minimal scarring.
Conclusion
Identifying a lipoma involves recognizing its distinct signs and symptoms, including its soft texture, mobility, and gradual growth. While lipomas are generally harmless, it is essential to monitor any changes in size, shape, or discomfort. Consulting a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation can provide peace of mind and help determine the appropriate course of action. Understanding the characteristics of lipomas can empower individuals to manage their health effectively and make informed decisions regarding treatment options.
